Get started¶
Use cases.
Load data¶
# Read *.ods or excel (spreadsheet).
data = pd.read_excel('D:\...\data2.ods', sheet_name=0,
skiprows=1).dropna(how='all')
data.name = 'data2'
Experiment subpackage¶
You can either use subpackages directly (physicslab.experiment.van_der_pauw)
or utilize the following batch function.
# Example: Van der Pauw
import pandas as pd
def load(filename):
data = pd.read_csv(filename + '.csv')
data.name = filename
return data
thickness = 1.262e-6 # meters
samples = ['sample#1', 'sample#2', ...]
data_list = [load(sample) for sample in samples]
results = physicslab.experiment.process(
data_list,
by_module=physicslab.experiment.van_der_pauw,
thickness=thickness
)
print(results)
sheet_resistance ratio_resistance sheet_conductance resistivity conductivity
units ohms per square 1 1/ohms square ohm m 1/ohm/m
sample#1 1.590823e+05 1.168956 6.286055e-06 0.200762 4.981026
sample#2 1.583278e+05 1.185031 6.316009e-06 0.199810 5.004762
...
Van der Pauw¶
Handling Geometry enum.
def get_geometry(orientation, direct):
"""
:param int orientation: Contacts rotation in multiples of 90°.
:param bool direct: Contacts counter-clockwise (True) or not.
"""
geometry = van_der_pauw.Geometry.R1234 # Default configuration.
geometry = geometry.shift(number=orientation)
if not direct:
geometry = geometry.reverse_polarity()
return geometry
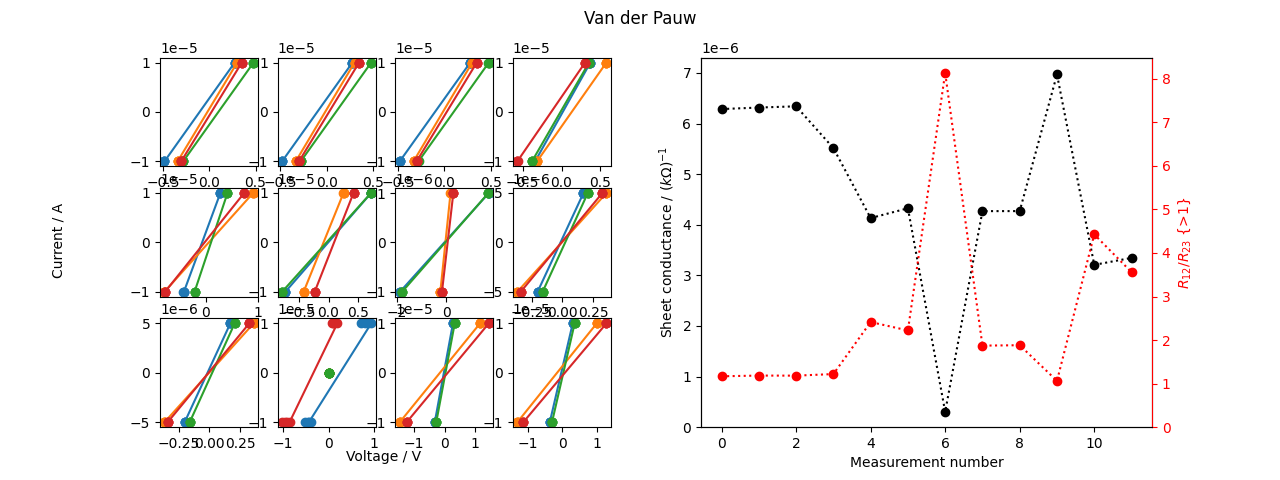
Plotting.
from physicslab.experiment import van_der_pauw
data_list = load(sample_name) # Custom function.
results = physicslab.experiment.process(data_list, by_module=van_der_pauw)
van_der_pauw.plot(data_list, results)
plt.show()
Magnetism type¶
results = physicslab.experiment.magnetism_type.process(measurement)
print(results)
cols = physicslab.experiment.magnetism_type.Columns
B = measurement[cols.MAGNETICFIELD]
plt.plot(B, measurement[cols.MAGNETIZATION], 'ko') # Original data.
plt.plot(B, measurement[cols.DIAMAGNETISM], 'r-') # Separated DIA contribution.
plt.plot(B, measurement[cols.FERROMAGNETISM], 'b-') # Separated FM contribution.
plt.plot(B, measurement[cols.RESIDUAL_MAGNETIZATION], 'g-') # Residual (unseparated) data.
plt.show()
curves.Line¶
line1 = Line(3, -2) # Line: y = 3 - 2x
line2 = Line(slope=2) # Line: y = 0 + 2x
line1(4.3) # -5.6
line1 - 5.3 + 2.4 * line2 # Line: y = -2.3 + 2.8x
line1.zero() # 1.5
Line.Intersection(line1, line2) # (0.75, 1.5)
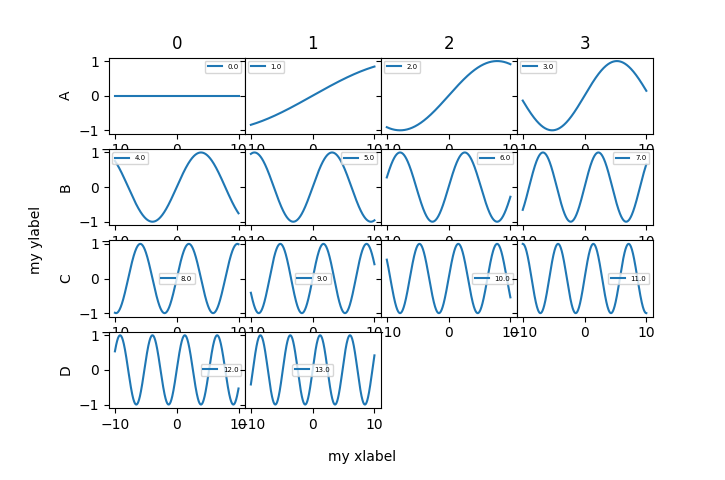
ui.plot_grid & utility.squarificate¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import physicslab
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, num=1000)
def plot_value(ax, value): # Sine.
ax.plot(x, np.sin(x * value / 10), label=value)
def alphabet(num): # ['A', 'B', ...]
return [(chr(ord('A') + i)) for i in range(num)]
data = np.arange(14, dtype=float) # E.g. a list of measurements.
data = physicslab.utility.squarificate(data) # Squarish 2D array distribution.
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=alphabet(data.shape[0])) # Naming.
df.name = 'My title'
print(df)
physicslab.ui.plot_grid(
df, plot_value, xlabel='my xlabel', ylabel='my ylabel',
subplots_adjust_kw={'hspace': 0}, sharey=True, legend_size=5)
0 1 2 3
A 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0
B 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0
C 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0
D 12.0 13.0 NaN NaN
Show images¶
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
# Show pictures (like SEM images). Parameter value is then e.g. a filename.
def plot_value(ax, value):
img = mpimg.imread(filepath)
ax.imshow(img, cmap='gray')